What is ADHD Disorder in Children?
What is ADHD Disorder in Children?
ADHD Disorder in children is a disorder that affects attention, impedes sitting still, and suppresses actions. It stands for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, the signs of which appear at the age of 2 and are more evident by the age of 6 years. This disorder is characterized by acting on impulse, not being able to sit in one place, and running around aimlessly. These actions are not due to poor parenting skills, laziness, or careless behavior – ADHD Disorder is a brain-based disorder and can impede some children. If parents or teachers are able to identify the Signs of ADHD early enough, they can provide the support needed to help children grow, moving forward with their learning.
Table of Content
Symptoms of ADHD Disorder in Children
Children with ADHD disorder cannot sit in one place for a long time, due to which they are fidgety. Children with ADHD frequently manifest behaviors that may be interpreted as carelessness or defiance, but which are actually manifestations of an attention-oriented disability. Typically, the symptoms of ADHD fall under three domains: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Children may show styles of ADHD with symptoms for all three domains or with symptoms from only one domain.
To download the brochure of the Diploma in SEN, click here!
For more information on a Diploma in SEN, Call/WhatsApp at +919321024137 / +919869866277
Common symptoms of ADHD Disorder in children include:
Inattention:
- Difficulty staying focused on tasks or play
- Frequent mistakes due to carelessness
- Trouble organizing tasks and belongings
- Easily distracted by surroundings or thoughts
- Forgetfulness in daily activities
Hyperactivity:
- Constant fidgeting or squirming
- Inability to sit still, especially in calm settings
- Excessive talking
- Running or climbing at inappropriate times
Impulsivity:
- Blurting out answers before a question is completed
- Difficulty waiting for their turn
- Interrupting others’ conversations or games
When these conduct patterns of the child are predominantly hampering the child’s daily functioning at school, home, and any social environments, these are the signs of ADHD disorder. When these signs are considered seriously and are recognized at an early stage, it becomes easy to understand the precise challenges faced by the child, and accordingly, a suitable intervention approach of proper strategies, support, and sometimes medical help is offered.

Causes of ADHD in Children
The exact causes of ADHD in children are not clearly known, but as per the latest findings, ADHD is a neurological condition that is caused due to a mix of genetic and environmental factors. There are certain baseless myths, such as bad parenting and too much junk food causes ADHD, although they might be an adding factor to already existing ADHD characteristics.
Knowing that many factors could influence ADHD may reduce the assumption of blame, so care can be enacted.
Possible causes of ADHD in children include:
Genetics:
ADHD often runs in families. If there is an existing case of ADHD in a family, there are higher chances of the next generation having an ADHD child as well.
Brain structure and function:
The brain’s areas that are in charge of processing and regulation skills are differently developed for ADHD individuals compared to those who do not have ADHD.
Poor birth weight
Babies born ahead of their actual due date have low weight, which can be a reason for developing ADHD.
Exposure to toxins:
When pregnant mothers are exposed to harmful chemicals, it directly impacts the foetus, aggravating the chances of children getting ADHD.
When pregnant mothers are addicted to tobacco-related substances, such as cigarettes or alcohol, it can increase the chances of children developing ADHD, as they affect the brain structure of unborn children.
Brain injury:
In some instances, there are chances of physical injuries that affect the frontal lobe in charge of attention skills.
Multiple factors often work together, and early support can make a big difference.
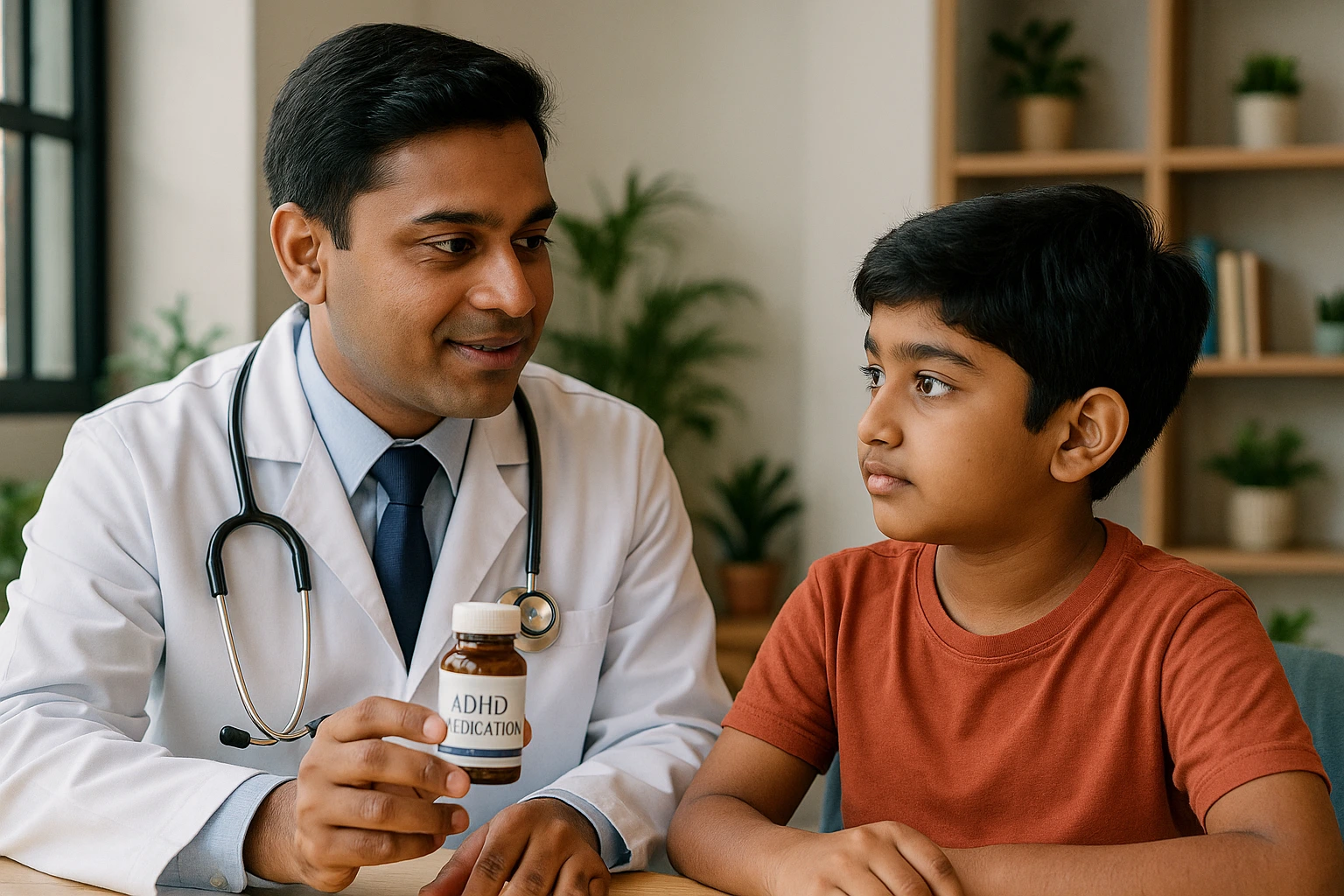
Treatments for Children with ADHD Disorder
ADHD is a neurological condition that has 3 main aspects that must be addressed, namely inattention, impulsive behaviours, and sitting in one place. To address these 3 different areas, a meticulously designed intervention approach comprising strategies and teaching pedagogies is to be utilized.
Devising a precise intervention plan combining a blend of effective strategies and teaching techniques helps children with ADHD with their attention span and manage their impulsive actions. An appropriate mix of academic, emotional, and behavioural strategic treatment has proven to help children with ADHD manage their routines better and support long-term progress.
Common treatments for children with ADHD Disorder include:
Behavioral therapy:
- This strategy focuses on helping the child to handle their trigger points and be unruffled.
- With the help of scheduling, rewarding children is encouraged to manage their emotions better.
Medication:
Depending on the effects ADHD has on children, at times, medical professionals may recommend some medication that helps to calm children down, helping them focus better and be less disruptive in their surroundings.
Parent training:
Parents are taught techniques to manage behavior, build positive routines, and support their child effectively at home.
Classroom support:
Teachers can change the classroom settings in such a way that helps children to stay focused and be calm while performing tasks and classroom activities.
Counseling or therapy:
This plays an essential role in providing children with much-needed emotional support and guidance to vent out their feelings and get rid of any anxiety and frustration that ADHD causes.
Daily routine changes
When the lifestyle of the child is much healthier with lesser screen time and better sleep patterns, it helps to tranquilize the brain and regulate behaviour.
Early and consistent support can greatly improve a child’s development and daily functioning.

Source: stock.adobe.com
Childhood ADHD Disorder Prognosis
As discussed earlier, ADHD has 5 distinct types, where each category affects specific skills and has varied challenges different for each type. Therefore, the type of support the child will receive depends on the kind of struggles the child is facing and whether he has received any targeted intervention earlier.
When the precise treatment is offered for the child, addressing his needs, the child gradually navigates his way to function independently.
Important aspects such as clear routines, energy-releasing breaks, and a healthy learning space can help to enhance the long-term ADHD prognosis.
Key points about the prognosis of ADHD Disorder in children:
- With regular therapy treatments and appropriate ADHD treatment, children can strive to In general, children with ADHD Disorder can improve their attention, self-regulation, and social skills given appropriate treatment and ongoing support.
- Some degree of symptomology may exist in adolescence or adulthood, but there is a difference in their adverse effects on education and relationships with early intervention.
- Children who receive behavioral interventions, medication if necessary, and academic modifications often perform better academically and socially.
Educators trained to support children with special needs are inherently part of the solution towards a good outcome. The Special Education Needs Course presented by Vidhyanidhi Education Society (Govt. Regd.) is designed to train teachers and caregivers to fully understand their role and responsibilities with children and their learning, and to make sense of their learning and behavioral challenges. The Special Education Needs Course provides real-life experiences and practical strategies. Parents and educators who complete a Special Education Needs Course are better equipped to support children with ADHD Disorder, leading to improved academic and emotional success.
Unlock your potential as a Special Education with Vidhyanidhi Education Society’s (Govt. Regd.) Diploma in SEN today!
To download the brochure of the Diploma in SEN, click here!
For more information on a Diploma in SEN, Call/WhatsApp at +919321024137 / +919869866277
FAQs
Is ADHD a learning disability?
No. ADHD alters focus and impulse control, not intelligence. It can occur alongside learning disabilities; early testing helps. Vidhyanidhi Education Society can guide.
What is the hardest age for ADHD kids?
The effects of ADHD are maximum with the onset of the 6th year and are highly impactful till 12 years, as during these crucial years, there is a major transition from preschooling to formal primary education.





